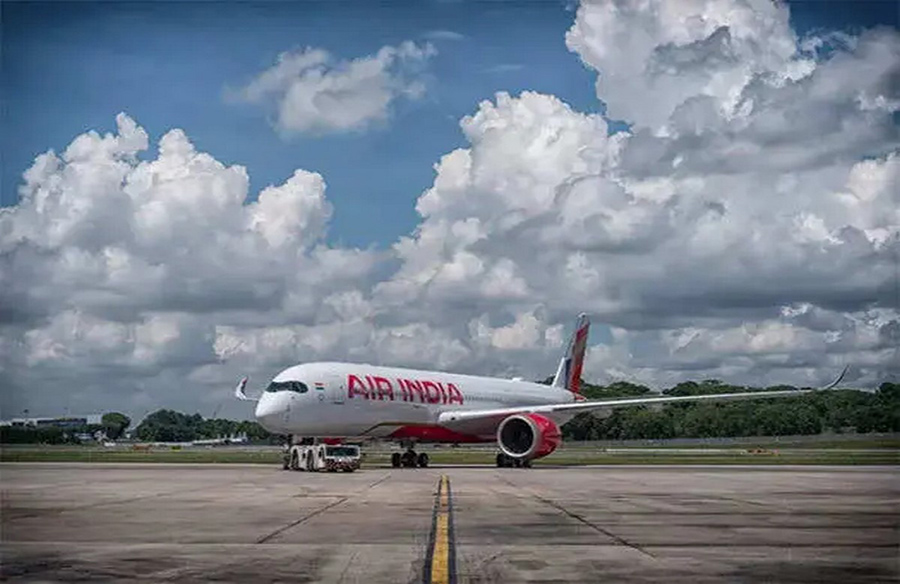
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) in India has decided to defer the implementation of the revised flight duty norms for pilots, which were initially slated to come into effect from June 1. This move follows consultations and considerations regarding the implications of the new norms on pilot rest and fatigue management.
Background and Context
The revised Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) norms were introduced with the aim of providing pilots with more rest time and addressing concerns related to pilot fatigue. However, the decision to defer the implementation indicates a need for further deliberation and discussions among stakeholders.
Wider Consultations and Thorough Considerations
According to civil aviation ministry officials, the deferment of the revised norms allows for wider consultations within the aviation sector. This decision comes shortly after the DGCA had initially communicated to airlines that there would be no deferral of the deadline for implementing the new FDTL norms.
Industry Feedback and Requests
The Federation of Indian Airlines (FIA), representing major carriers like Air India, SpiceJet, and IndiGo, had requested more time for the implementation of the revised norms. The FIA’s communication highlighted the need for careful consideration and preparation before implementing the changes outlined in the revised FDTL norms issued earlier this year.
Key Changes in the Revised Norms
Among the key changes proposed in the revised FDTL norms are increased weekly rest time for pilots, limitations on the number of landings during night operations, and extension of night hours for pilots. Additionally, airlines are required to submit quarterly fatigue reports, emphasizing a non-punitive and confidential approach to fatigue management.
Implications and Future Steps
The decision to defer the implementation of the revised FDTL norms reflects a balanced approach, considering the complex nature of aviation operations and the importance of ensuring pilot well-being and safety. Moving forward, thorough consultations and assessments will likely guide the eventual implementation of these norms to enhance operational efficiency while prioritizing pilot rest and fatigue management.